Running a Java application as a system service on Ubuntu 20 or 22 ensures it starts automatically on boot, restarts on failure, and can be managed efficiently. This guide provides a detailed walkthrough for setting up your Java app as a service, configuring logging, managing resources, and ensuring stability.
Running your Java application as a service provides:
Automatic startup: Your app launches automatically when the system boots.
Process management: Easily start, stop, or restart the app without manual intervention.
Resource control: Limit CPU and memory usage to maintain server stability.
Logging: Track application output for monitoring and debugging purposes.
User isolation: Run the app under a specific user for security and separation from other processes.
This setup is particularly useful for hosting Java backends on Linux servers like an EgyVPS instance. It ensures reliability, scalability, and easier management in production environments.

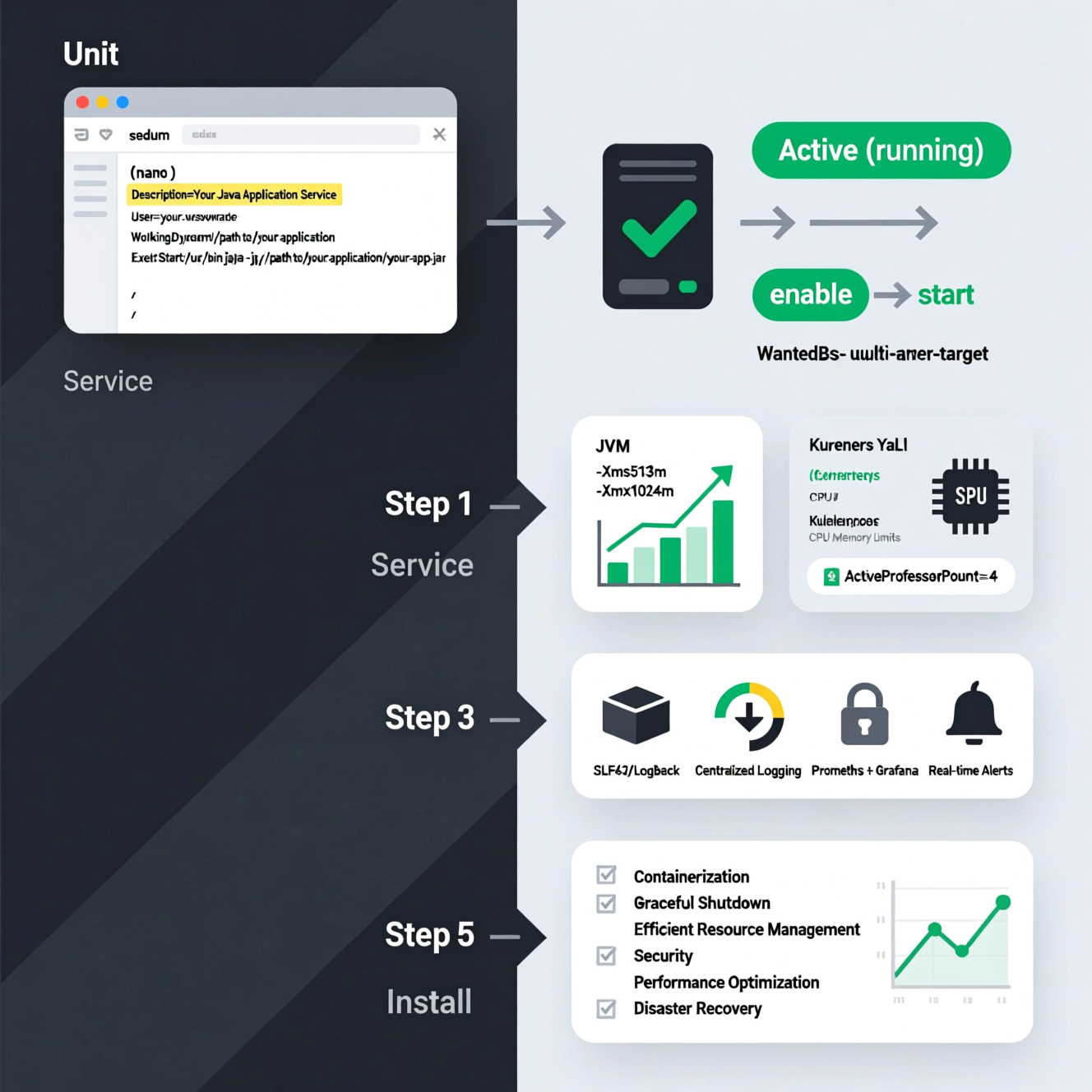
Open a terminal and create a new service file:
Add the following content, updating paths and usernames:
Explanation:
User: The account under which the Java app runs.
WorkingDirectory: Directory containing your .jar file.
ExecStart: Full command to launch the application.
This setup ensures that your application runs under a dedicated user account, improving security and process isolation.
Check status: sudo systemctl status your-app.service
Stop or restart: sudo systemctl stop your-app.service or sudo systemctl restart your-app.service
Enabling the service ensures it will start automatically on every system boot, reducing manual maintenance.
Memory Limits:
JVM options: -Xms for initial heap, -Xmx for max heap.
Example: java -Xms512m -Xmx1024m myapp.jar
CPU Limits:
In containerized environments like Docker or Kubernetes, define CPU requests and limits.
Example Kubernetes spec:
Use -XX:ActiveProcessorCount= in JVM to optimize CPU usage.
Proper resource management prevents performance bottlenecks, ensures fair usage, and avoids crashing the server due to runaway processes.
Effective logging and monitoring help maintain application health:
Use SLF4J or Logback for structured logging.
Store logs in files or send them to centralized logging tools.
Integrate with Prometheus and Grafana for real-time monitoring.
Set up alerts to detect performance issues, memory leaks, or failures proactively.
Logging not only helps in debugging but also aids in capacity planning and system optimization.
Containerization: Package the app with its dependencies in Docker for consistency across environments.
Service Wrappers: Use systemd on Linux, or NSSM/Launch4j on Windows to run Java apps as native services.
Efficient Resource Management: Optimize memory, CPU, database connections, and caching strategies.
Graceful Shutdown: Ensure proper resource cleanup and implement slow-start mechanisms.
Security: Secure secrets, update dependencies, and implement robust authentication.
Performance Optimization: Profile critical sections, use multithreading, and optimize queries.
Disaster Recovery: Implement backups and high-availability setups with load balancing and failover.
Testing and Maintenance: Regularly update JVM, libraries, and OS packages; perform routine monitoring and load testing.
Systemd allows Java apps to run reliably as services on Ubuntu 20/22.
Proper CPU and memory limits ensure stability and prevent performance degradation.
Logging, monitoring, and efficient startup/shutdown improve reliability.
| Feature | Systemd Service | Docker/Kubernetes |
|---|---|---|
| Startup | Managed by systemd | Managed by container orchestrator |
| Resource limits | Manual JVM options | Requests & limits defined in spec |
| Isolation | Linux user isolation | Full container isolation |
| Logging | journalctl or file logs | Centralized container logs |
| Scalability | Limited to server | Easy scaling across nodes |
Both approaches have pros and cons: systemd is simpler for single servers, while containerized deployments offer better portability, isolation, and scalability.
Q1: Can I run multiple Java services on the same server?
Yes, each service should have a separate systemd file and dedicated user if possible.
Q2: How do I view logs for my Java service?
Use journalctl -u your-app.service or configure logging to a file within your application.
Q3: Can I adjust CPU/memory limits after setup?
Yes, update the service file, container spec, or JVM options and restart the service.
Q4: Will the service start automatically after a reboot?
Yes, if you used systemctl enable your-app.service.
Q5: Is this setup compatible with Ubuntu 20 and 22?
Absolutely, systemd works on both versions.
هل تحتاج إلى Windows VPS سريع وآمن وبسعر مناسب؟
شركة EgyVPS بتوفرلك سيرفرات ويندوز جاهزة للاستخدام فورًا.
? تواصل معنا عبر: 201001197157
? أو زور موقعنا: https://egyvps.com