Choosing the right VPS for your Java applications is critical. Proper allocation of resources, storage type, and OS selection directly affect your application’s performance, reliability, and scalability. Whether you are deploying a small web application or a large enterprise system, understanding your Java server requirements is the first step toward optimal deployment.
Linux vs Windows: Most Java applications perform better on Linux due to lower overhead and better compatibility with JVM and open-source tools. Windows may be preferred if your team is familiar with it or if the application depends on Windows-only features.
Licensing Costs: Linux distributions like Ubuntu, CentOS, or Debian are free, while Windows Server licenses add extra cost to your VPS plan.
CPU: Java applications can be CPU-intensive, especially when handling complex computations, large datasets, or high concurrency. Multi-core processors improve performance significantly.
RAM: JVM performance depends heavily on available memory. For small apps, 2-4 GB is sufficient, while enterprise applications with high traffic may require 8 GB or more.
Disk Storage: SSDs provide faster read/write speeds compared to HDDs, reducing application startup time and improving database performance.
Networking: Ensure static IPs, properly configured open ports, and sufficient bandwidth for your expected traffic.
JDK Compatibility: Make sure your VPS allows installation of the required Java Development Kit version.
Application Servers: Common choices include Tomcat, WildFly, Jetty, and JBoss. The choice affects CPU and memory usage.
Database Support: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and other relational databases require adequate resources.
Firewall & Security: Proper firewall rules, DDoS protection, and secure access configurations are essential for production servers.
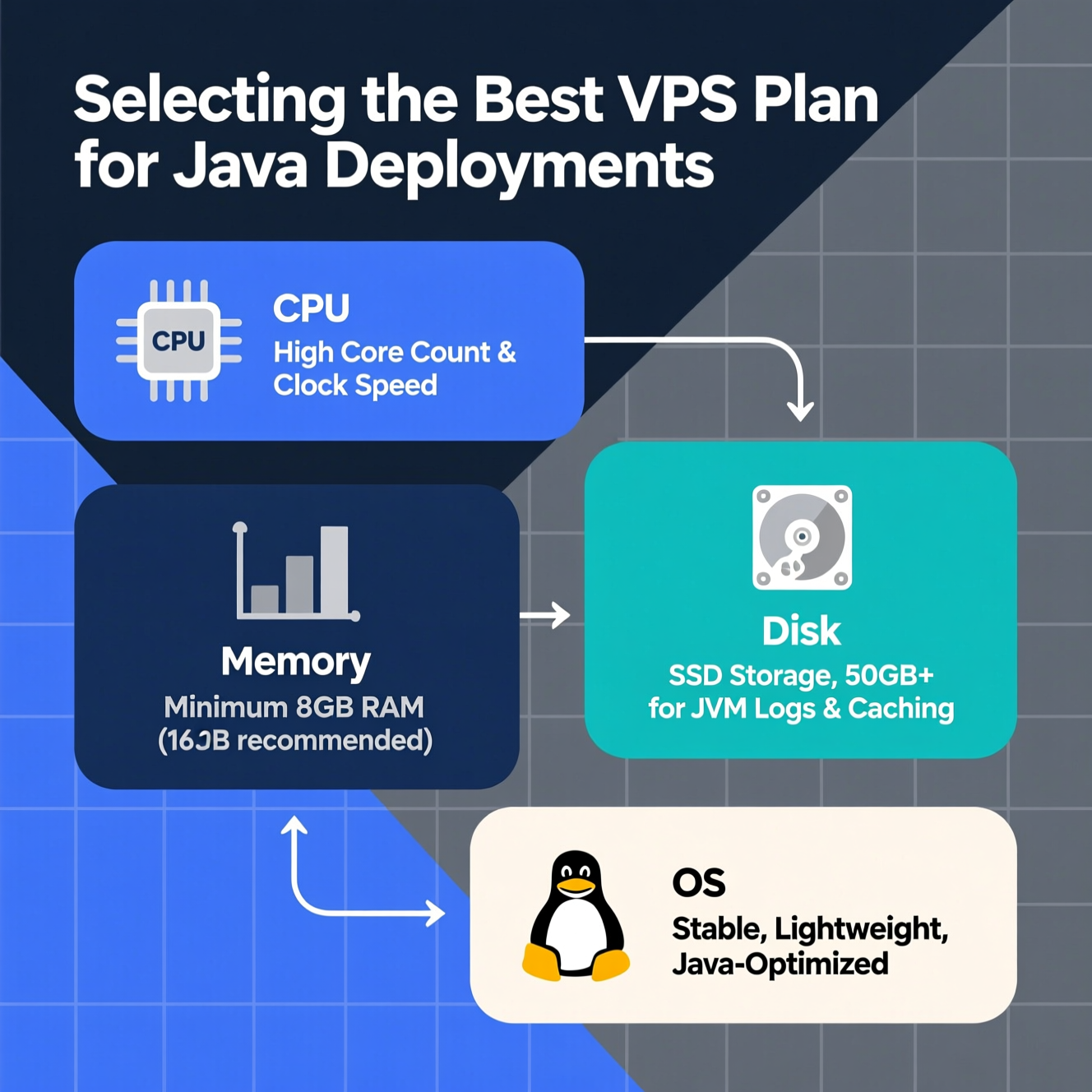
The number of CPU cores and clock speed determine how efficiently your Java applications handle multiple simultaneous requests.
For small applications: 1-2 cores may suffice.
For medium traffic: 2-4 cores recommended.
For large-scale applications: 4 cores or more, possibly with high-performance CPUs.
JVM memory allocation is critical to prevent frequent garbage collection, which can degrade performance.
Minimum recommended RAM: 2 GB for small apps.
Medium apps: 4-8 GB.
High-traffic enterprise apps: 8-16 GB or more.
SSD vs HDD: SSD is recommended for high-performance applications and fast database access. HDD can be used for backups or archival purposes.
Ensure enough storage for OS, JDK, application server, application files, and database data. Starting at 40-50 GB SSD is recommended.
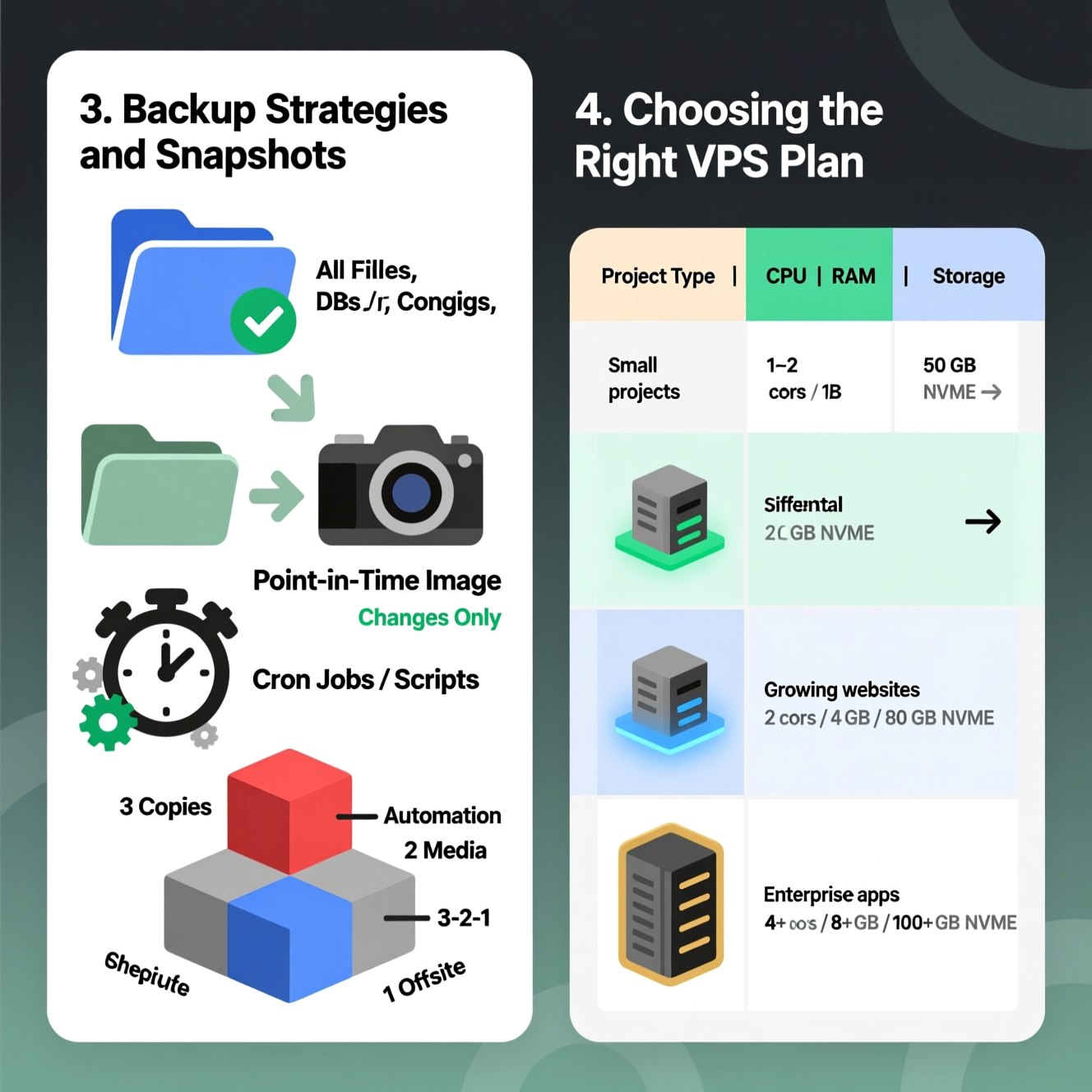
Full Backup: Copies all application files, databases, and system configuration.
Incremental/Differential Backup: Saves changes since the last backup, saving space and time.
Snapshots: Create point-in-time images of your VPS for fast recovery.
Automation: Use cron jobs or scripts to schedule backups regularly.
3-2-1 Rule: Keep three copies of your data, store them on two different mediums, and maintain one copy offsite.
Testing: Regularly test backup restoration to ensure reliability in case of failure.
Ensure sufficient CPU cores, RAM, and SSD storage.
Choose an OS compatible with Java and your application server.
| Project Type | CPU | RAM | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small projects | 1-2 cores | 2 GB | 50 GB NVMe |
| Growing websites | 2 cores | 4 GB | 80 GB NVMe |
| Enterprise apps | 4 cores | 8 GB | 160 GB NVMe+ |
Pick VPS plans that allow easy upgrades of CPU, RAM, and storage as your traffic or data grows.
Update your server packages.
Install JDK, Maven, and application servers.
Create a non-root user for better security.
Use SCP or SFTP to upload your .jar or .war files.
For .jar files, run with java -jar your-app.jar.
For .war files, deploy to Tomcat or another application server.
Optionally, configure the app to run as a system service (systemd/init.d).
Install and configure MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle.
Set database connection properties in your app configuration (application.properties, web.xml, etc.).
Monitor performance using VisualVM, Spring Cloud, Zipkin.
Secure connections with SSL/TLS.
Optimize app performance using Microservices or load balancing.
SSD: High-speed performance, low latency, ideal for core application files and databases.
HDD: Lower cost, larger capacity, best for backups and archival storage.
Hybrid Approach: Use SSD for active applications and HDD for backup storage to balance performance and cost.
Regularly monitor CPU, RAM, and disk usage.
Automate backups and snapshots.
Start with a medium plan if unsure, and scale as needed.
Take advantage of promotional offers for long-term VPS subscriptions.
Test backup restorations periodically to ensure reliability.
Selecting the best VPS for Java applications involves careful consideration of CPU, RAM, storage, OS, backups, and security. Choosing a scalable VPS plan with SSD storage, proper backup strategy, and monitoring ensures stable, high-performance, and reliable Java deployments.
هل تحتاج إلى Windows VPS سريع وآمن وبسعر مناسب؟
شركة EgyVPS بتوفرلك سيرفرات ويندوز جاهزة للاستخدام فورًا.
? تواصل معنا عبر: 201001197157
? أو زور موقعنا: https://egyvps.com